Trusts in the UAE
Publications Written by Marsel Shadmanov

What is a trust?
First of all, it is essential to understand the concept. A trust is an agreement under which a person (a settlor of the trust) transfers his assets to a trustee, which undertakes to own and manage the assets according to interests of beneficiaries. When a settlor of the trust transfers his property (money, securities, real estate or other assets) to the trustee, he loses the right of legal ownership over the assets, but still with possibility to retain citeran control. This is the most important feature of a trust, since it allows to exclude property claims from, for example, creditors of a settlor.
The trust is usually governed by the trust deed, which outlines the terms of the trust, duration, list of beneficiaries, powers of a trustee, etc. A trustee owns and manages the assets according to the trust deed and receives remuneration for its work. Moreover, for a stronger supervision, a settlor may appoint a protector, who acts as a supervisor over trustee. Besides managing the assets, a trustee distributes the income according to the trust deed among the beneficiaries of the trust, prescribed by the settlor. The scheme of general trust structure is given below.
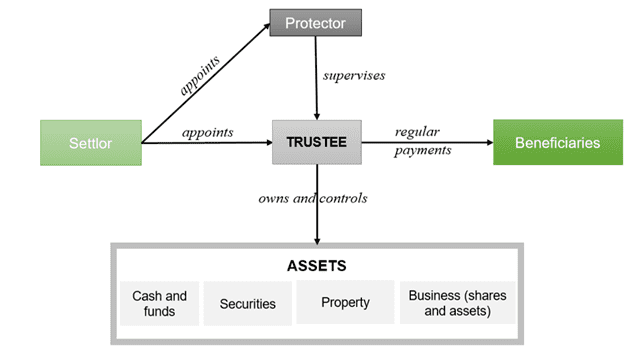
Trusts сan be established for a certain period (for example, for a lifetime of a settlor) or indefinitely. If the life period of trust expires, the property is distributed as specified in the trust deed (for example, it is returned to settlor or transferred to beneficiaries).
It should be noted that trusts usually do not constitute a legal entity, and are considered mostly as a contractual relationship, rather than a company. However, there are exceptions to this approach, for example, in the UAE, as will be explained below.
When can trusts be useful?
Trusts are used for a variety of reasons, the main of which include:
- Wealth Preservation and Succession planning. Trust can help to secure a safe transfer of wealth in case of succession and ensure the businesses and assets will continue to operate in adequate manner.
- Asset protection. Due to the fact that a settlor does not appear to be an owner of the assets, neither settlor`s creditors nor public authorities can address their claims against the aforesaid assets.
- Tax planning. By building the right structure involving a trust, you can avoid inheritance tax and minimize your income or capital gains tax liability.
- Confidentiality. A trustee, a protector and any other persons are not entitled to disclose any information about the trust, trustees, founder or beneficiaries, as well as information on the accounts and property of the trust. Moreover, many countries have publicly accessible registries of companies, but do not disclose trusts in such registers.
How trusts are regulated in UAE?
As a legal phenomenon, trusts mostly exist in countries of common law. Nevertheless, the UAE being a country of civil law have also introduced trusts into their regulatory framework in order to satisfy possible needs of entrepreneurs and high-net worth individuals.
On the federal level, current legislation, namely UAE’s 2020 Trust Law, allows to establish trusts in the country. Importantly to note, trusts in the UAE are considered to be a legal entity, which is a significant departure from the Anglo-American concept of a trust. The UAE Trust Law establishes a new entity which most closely constitutes a civil law statutory foundation entities. In particular, assets can be held and registered directly in the name of a trust, and a trustee has functions which are more similar to those of general managers in the context of limited liability companies.
Considering each emirate in the UAE may have its own regulations, Dubai has also acknowledged the trust and enabled the Trust Law in 2018. This law of the emirate provides for trusts to be established in the Dubai International Financial Center (DIFC), one of the most reputable free zones of the emirate. In fact, the DIFC free zone is the only location in Dubai where a trust can be established. In March 2022 some amendments were introduced to Trust Law of 2018 in order to bring the Trust Law in accordance with Financial Action Task Force`s (FATF) recommendations. This reflects the up-to-date character of trust regulation in Dubai.
It is important to note that the UAE Trust Law does not apply to trusts created in DIFC. Therefore, the process of trust`s registration and requirements may differ depending on type of a trust.
How to establish trust under the UAE Trust Law?
Trust may be created by one of the two following means: issuing of the Trust Instrument or drafting a Will (which comes into effect after the death of a settlor). After drafting one of the said documents, a settlor or a trustee file an application for introducing the trust document into the Register, which is managed by UAE Ministry of Finance. The trust shall come into effect upon completion of trust document registration. The competent authority will issue an official certificate and a list of the properties included in the trust. From this moment a trustee shall have the authority to sign the documents related to the trust property, with no need for the intervention of the settlor or the beneficiary.
It should be mentioned that the practice of establishing trusts under the UAE Trust law is not developed. Many questions remain unregulated. Therefore, it might be more practical to establish a trust in DIFC, which has more extensive experience in registering and maintain trusts under its jurisdiction.
How to establish a trust in Dubai (DIFC)?
Establishment of a trust in Dubai is supervised by the DIFC Authority and is available to both local and foreign individuals interested in using this type of asset management. There are the following types of trusts in the DIFC:
- charitable trust (a trust or portion of a trust, created for a charitable purpose);
- non-charitable or purpose trust (the purpose of holding or investing in shares in a company or juridical person or any other assets);
- express trust (a trust created with the settlor’s express intent declared in writing or a written declaration of trust by the trustee);
- protective trusts (a trust that is designed to protect the trust property to ensure the continued support of the beneficiary).
When starting the registration process, the first step is a preparation of trust instruments (documents). There are two ways for creating a trust in Dubai: by drafting a will or by preparing a deed of trust (named as codicil in the Trust Law). Drafting these documents is not an easy task because you have to both satisfy the regulatory requirements and meet interests of a settlor. That is the key stage as well-prepared trust instrument will determine the possibility of challenging the trust`s validity and claims against parties involved. Apparently, a trust instrument which is inconsistent with the applicable regulations will not be approved by the DIFC Authority.
As you can understand from the text of the Trust Law, it provides for many detailed requirements to validity of a trust, powers of trustees, features of contributed assets, etc. This must be analyzed in detail before establishing a trust.
We will be glad to help you to orient in trust regulations of UAE and Dubai in particular, and assist with establishment of a trust meeting your goals the most.
Marsel Shadmanov
Head of Corporate Services at Garant Business Consultancy DMCC
Phone +971 4 421 4335
Email info@garant.ae